How To Find Instantaneous Rate Of Change In Excel This video demonstrates how to estimate the instantaneous rate of change of a function at a point using Excel
This video explains how to use a table of values to determine average rates of change to estimate an instantaneous rate of change https mathispower4u 3 Compute the instantaneous rate of change of the function g t e t at t 1 4 Determine the instantaneous rate of change for the function h x ln x at x 1 5 For the function g t 5t 7 calculate the average rate of change over the interval from t 2 to t 5
How To Find Instantaneous Rate Of Change In Excel
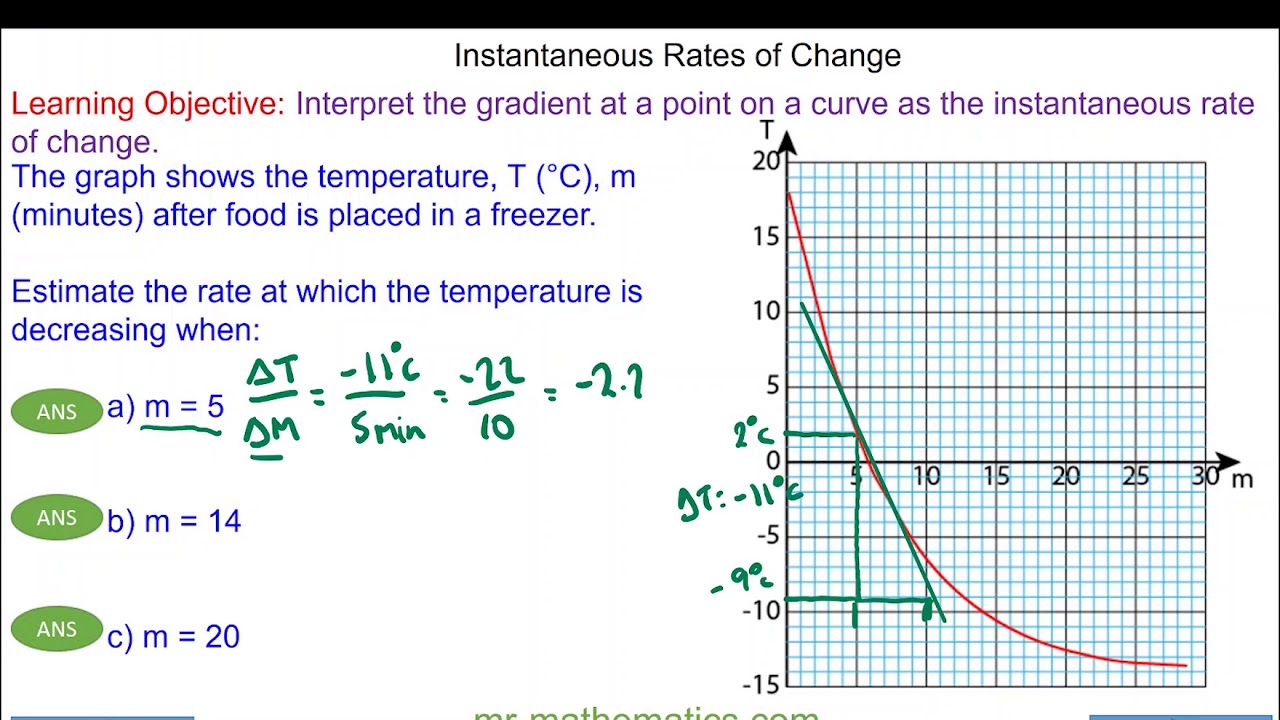
How To Find Instantaneous Rate Of Change In Excel
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/e47yR5vkve4/maxresdefault.jpg

Zero Instantaneous Rate Of Change YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ict5qduIl0c/maxresdefault.jpg
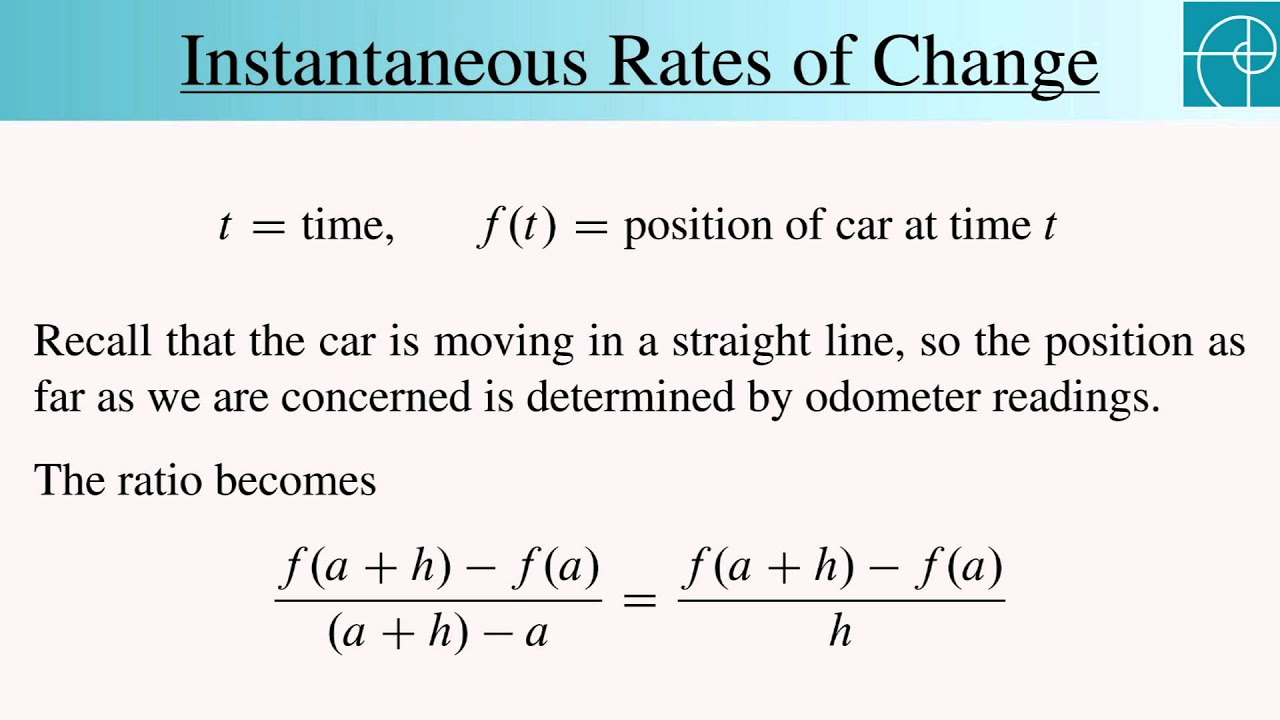
Instantaneous Rates Of Change YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TQyc9M6zQGQ/maxresdefault.jpg
I hate to be a stickler but that s not technically a derivative formula until limits are involved That formula provides a rate of change yes but it doesn t narrow it down to an infentesimally small point on the curve to show an instantaneous rate of change Rise over run does not constitute a derivative but rather a slope m in your linear formula How to find Instantaneous Rate of Change You can calculate instantaneous rate of change at a point as follows Input First of all just Enter the function or equation in the respective input filed Now enter the value of x you can select negative or positive as per your need Click the calculate button Output
The average rate of change shows how a function changes over time The instantaneous rate of change on the other hand shows how a function changes at a single point Instantaneous rate of change The instantaneous rate of change of a function f x at a point x a is defined as the limit of the average rate of change as the interval approaches zero The instantaneous rate of change is the change in the rate at a particular instant and it is same as the change in the derivative value at a specific point For a graph the instantaneous rate of change at a specific point is the same as the tangent line slope That is it is a curve slope
More picture related to How To Find Instantaneous Rate Of Change In Excel
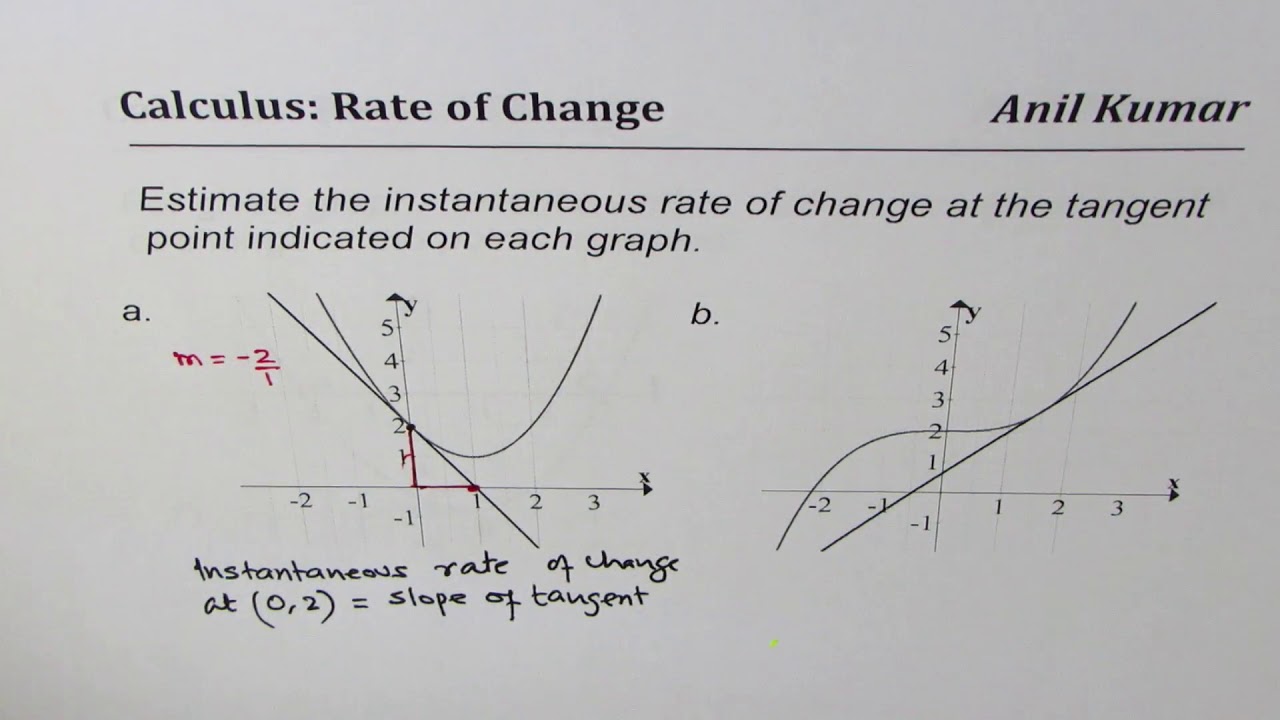
How To Calculate Instantaneous Rate Of Change From Graph YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/izCzyujhuYs/maxresdefault.jpg

Instantaneous Rate Of Change Quadratic Function YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/6IGOrFfXvaE/maxresdefault.jpg
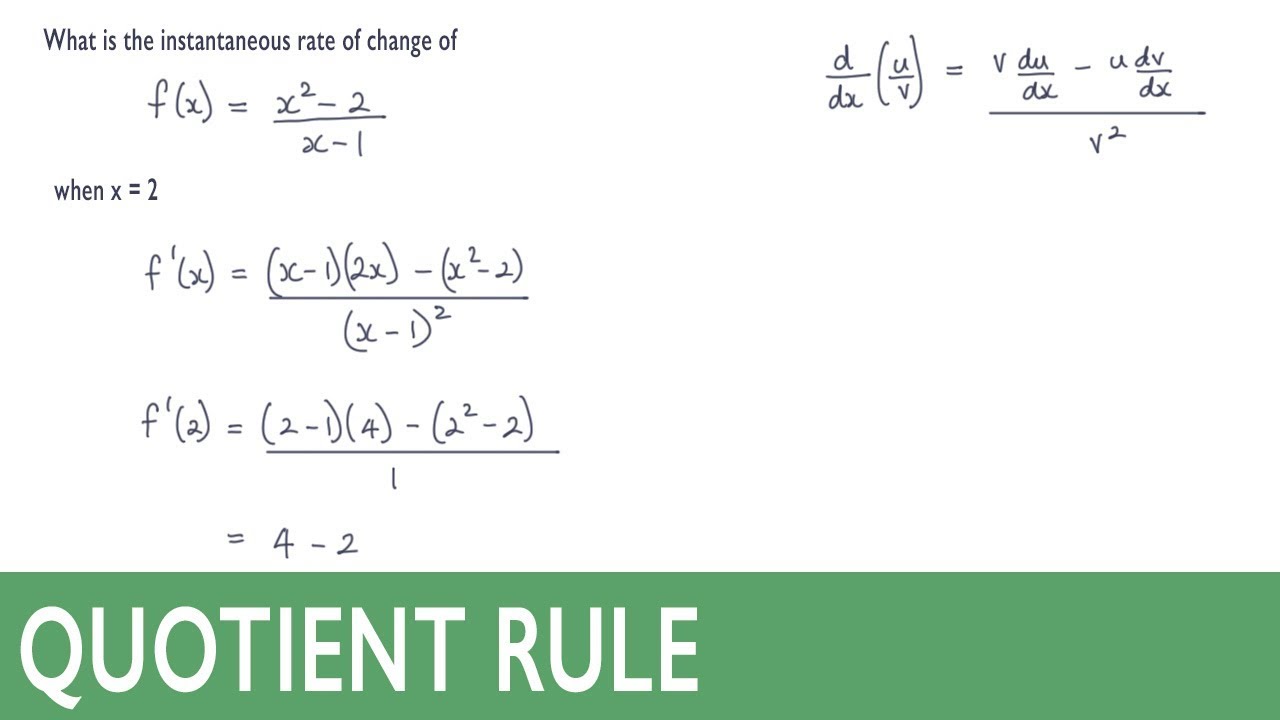
Instantaneous Rate Of Change Using The Quotient Rule YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nlj6Kfg46Sc/maxresdefault.jpg
The instantaneous rate of change is the change in the concentration of rate that occurs at a particular instant of time The variation in the derivative values at a specific point also denotes the instantaneous rate of change The instantaneous rate of change at a point is equal to the derivative function evaluated at that point Calculating Rate of Change in Excel Now that your worksheet is ready let s calculate the rate of change This is where Excel shines handling the math so you don t have to To calculate the rate of change you ll use a simple formula Click on the cell where you want the result to appear
[desc-10] [desc-11]
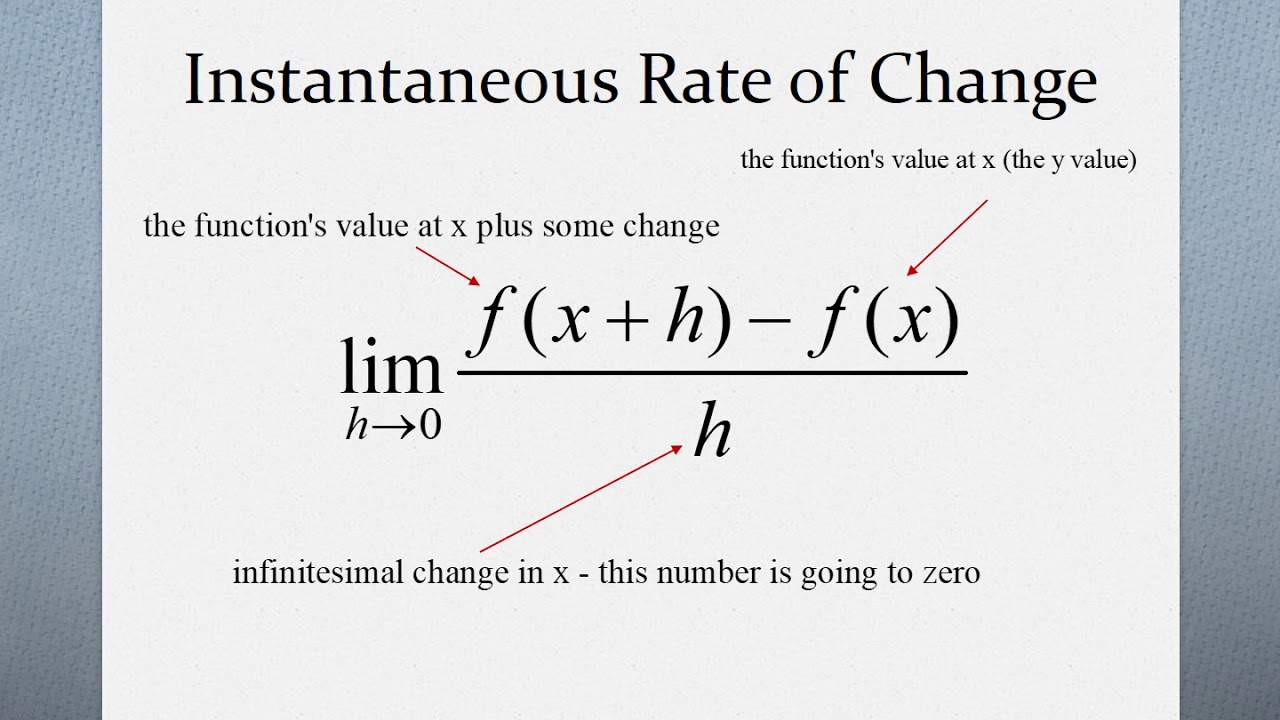
Instantaneous Rate Of Change Of A Function YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/bafE42IKhs8/maxresdefault.jpg
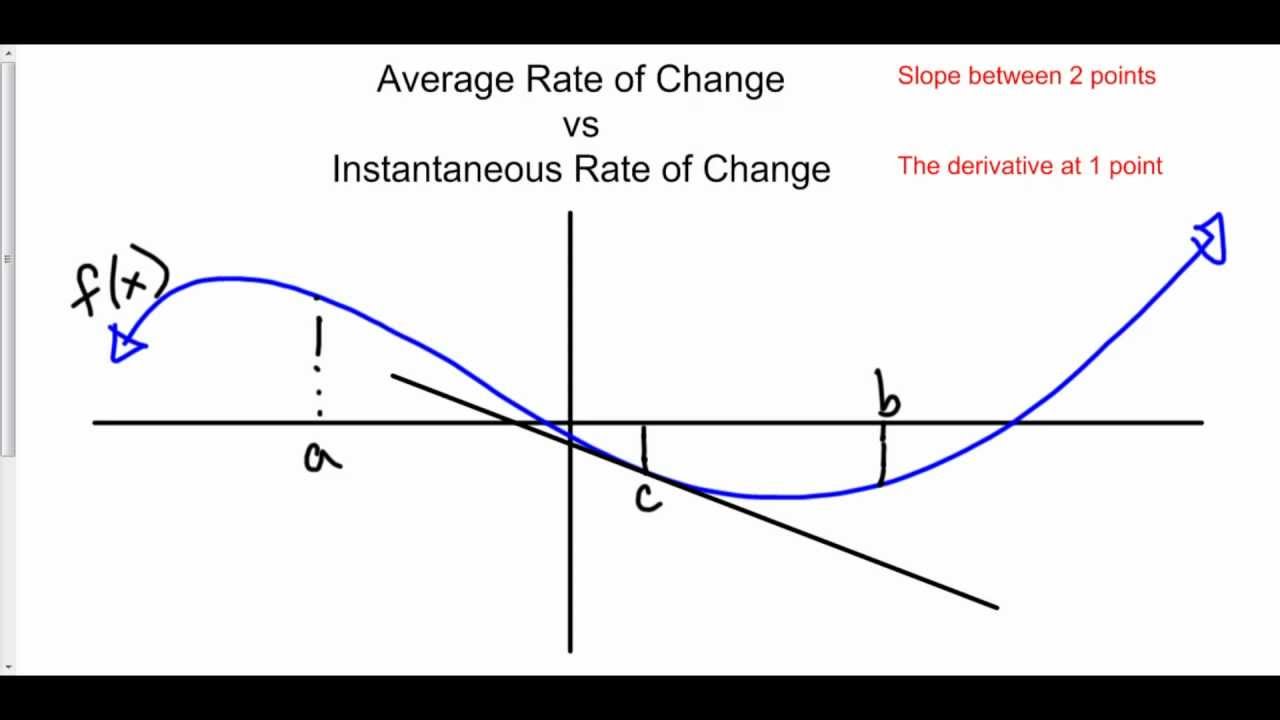
Average Vs Instantaneous Rate Of Change YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/J7VbhV_yp2U/maxresdefault.jpg
How To Find Instantaneous Rate Of Change In Excel - I hate to be a stickler but that s not technically a derivative formula until limits are involved That formula provides a rate of change yes but it doesn t narrow it down to an infentesimally small point on the curve to show an instantaneous rate of change Rise over run does not constitute a derivative but rather a slope m in your linear formula